RFID vs. Barcode: Similarities, Differences, Pros for your Business
Every day, enterprises worldwide make crucial decisions to increase productivity and decrease costs. This objective can be accomplished by modernizing businesses with RFID or barcodes scanning.
Business owners adopt RFID and barcode technology for asset and inventory tracking. These technologies are utilized in several sectors such as logistics, retail, manufacturing, and healthcare. Both solutions share similarities; thus, many people sometimes mistake one after the other.
In this article, we will better introduce you to RFID readers. We will compare RFID with barcode technology and explain their differences. By the end, you will be able to make a more informed decision on how to successfully run your business and increase your Return on Investment (ROI).

Barcode Technology Explained
A barcode can be described as a data representation in code. Essentially, it is an image that consists of a series of parallel black and white bars, which are read by an optical scanner.
Generally, barcodes are applied to products to identify them during inventory tracking. Among their different applications, barcodes are often used in retail stores as part of the purchasing process, and in warehouses to manage inventory.
After gathering the information, barcode scanners connect to a host computer transmitting information in real-time, without additional human intervention. This property effectively helps retailers automate data collection processes and reduce human errors.
This solution supports mainly two types of scanning methods: 1-Dimensional and 2-Dimensional scanning .
1-D is quite simple, it can mainly store text data and product prices. On the other hand, 2-D is more complex because it includes information such as prices, quantities, and images.
RFID Technology Explained
According to a recent report, the worldwide RFID industry is projected to expand massively. Within 2026 RFID market value is expected to reach 17.4 billion USD at a CAGR of 10.2%.
Radio Frequency-Identification (RFID) is a technology that uses radio waves to identify tagged items. RFID systems consist of three main components: a scanning antenna, a transceiver, and a transponder. The scanning process involves an RFID reader (stationary or mobile) to scan the item tag.
In a nutshell, the antenna conveys a radio-frequency signal that activates the tag. Once activated, the tag sends out a wave back to the antenna, where it is translated into data. RFID technology has seen numerous applications in logistics, retail, healthcare, and customer experience. Overall, tags have a stronger power source and a longer read range than barcodes.
Barcode vs. RFID: Similarities and Differences
At the beginning of this article, we have reported that most people have a hard time differentiating RFID and barcode technology.
So, what are the similarities between these two solutions?
Both technologies are used for asset and inventory tracking. RFID and barcode share many common applications, and they both utilize scanners or readers to retrieve information.
On the other hand, RFID and barcode differ greatly in implementation costs and functions. To briefly summarize, the barcode can scan in close proximity and a straight line. In addition, barcodes are very simple to use, yet they can just read data. This characteristic can be both a limitation and an advantage depending on your needs. Barcodes generally are very precise as they can scan just one item at the time.
By contrast, RFID readers can scan multiple items together at long distances (10's, 100's, 1000's items simultaneously). RFID readers not just quickly read tags data, but they can modify them. RFID technology can better customize and manage information. For instance, you can maintain a product's history and record expiry dates.
RFID Technology Pros and Cons
RFID technology can bring numerous key advantages for your business. For example, RFID readers can increase efficiency by simultaneously scanning multiple tags at long-range. The radio wave is so potent to go through objects and they do not require scanning in a straight line to read data.
RFID automatically collects data reducing human effort, and uniquely identifies each item/asset tagged. Ultimately, RFID readers are extremely secure and reliable as the device's information is encrypted.
As for the disadvantages, more functions and higher performance come with a higher starting price. RFID tags cost is higher than barcodes as they are equipped with built-in chips.
At the same time, RFID readers' signals may be negatively impacted by materials such as liquid and metals.

Urovo RFID Solution
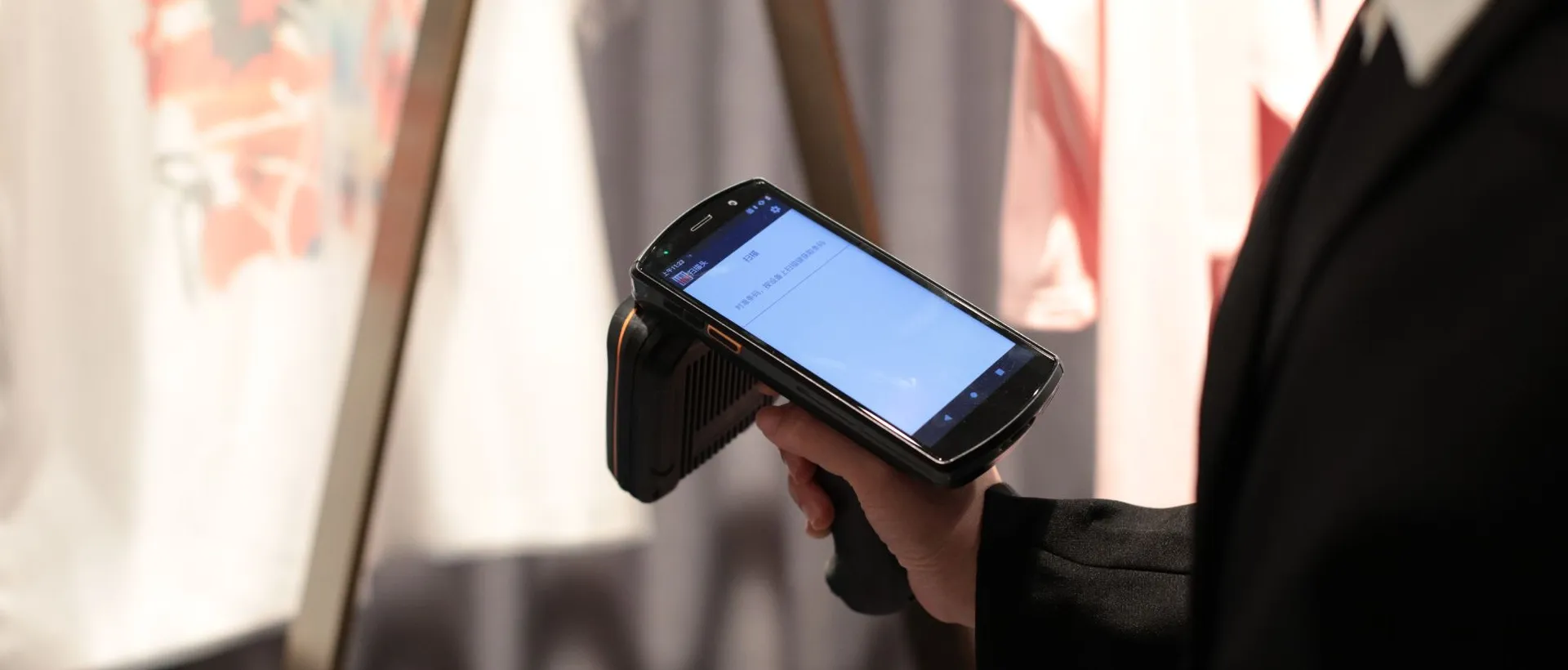
With your business success in mind, at Urovo, we have developed the new DT50 RFID reader. Urovo DT50 UHF RFID Smart Handheld Terminal enhances productivity by tracking assets and managing the inventory process.
Our RFID reader offers better quality and traceability. With its internal 5dBi high-sensitivity RFID antenna, the DT50 reader can cover a more comprehensive scanning range reaching up to 20m.
The device can effectively scan for various souses, including 1D/2D//distorted/stained/old barcodes. In addition, the DT50 can scan 100's of tags within a complex environment with metal interference. Thanks to our patented adaptive interference cancelation (SJC) technology, this breakthrough was made possible.
For improved production or warehouse inventory control, the DT50 reader's rugged nature can uninterruptedly scan for 2 hours even in harsh environments such as extremely low temperature ( -20~+60°C). You can rest assured by implementing the device as it complies with ISO/IEC 18000-63/64 high-quality standards.
Urove gladly puts its 15 years of experience in PDAs solution development to support your business success.We hope this article helped to clarify the main similarities and differences between RFID and barcode technology.
Contact us today to unleash the potential that this technology has in store for your business.