RFID Reader vs. Barcode Scanner: Which is Right for Your Business?
In the realm of asset tracking and inventory management, businesses face a crucial choice between two leading technologies: RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) reader and barcode scanner. This detailed comparison aims to equip decision-makers with the knowledge to select the right technology for enhancing operational efficiency and accuracy.

What is RFID reader?
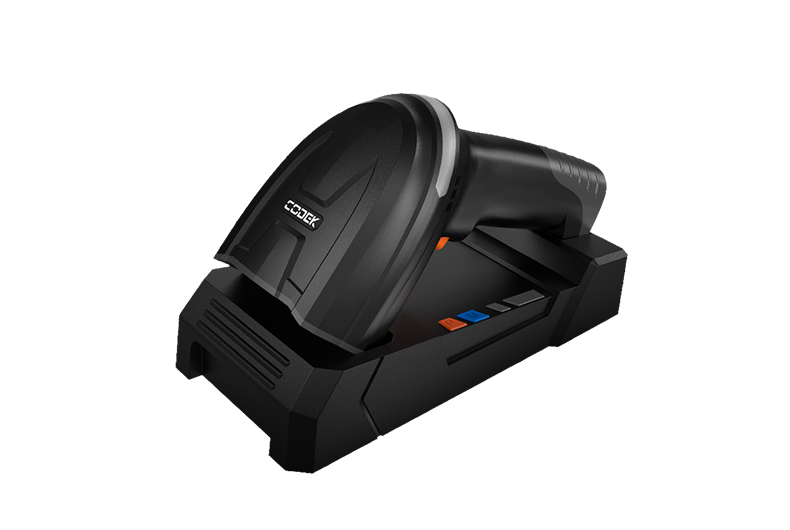
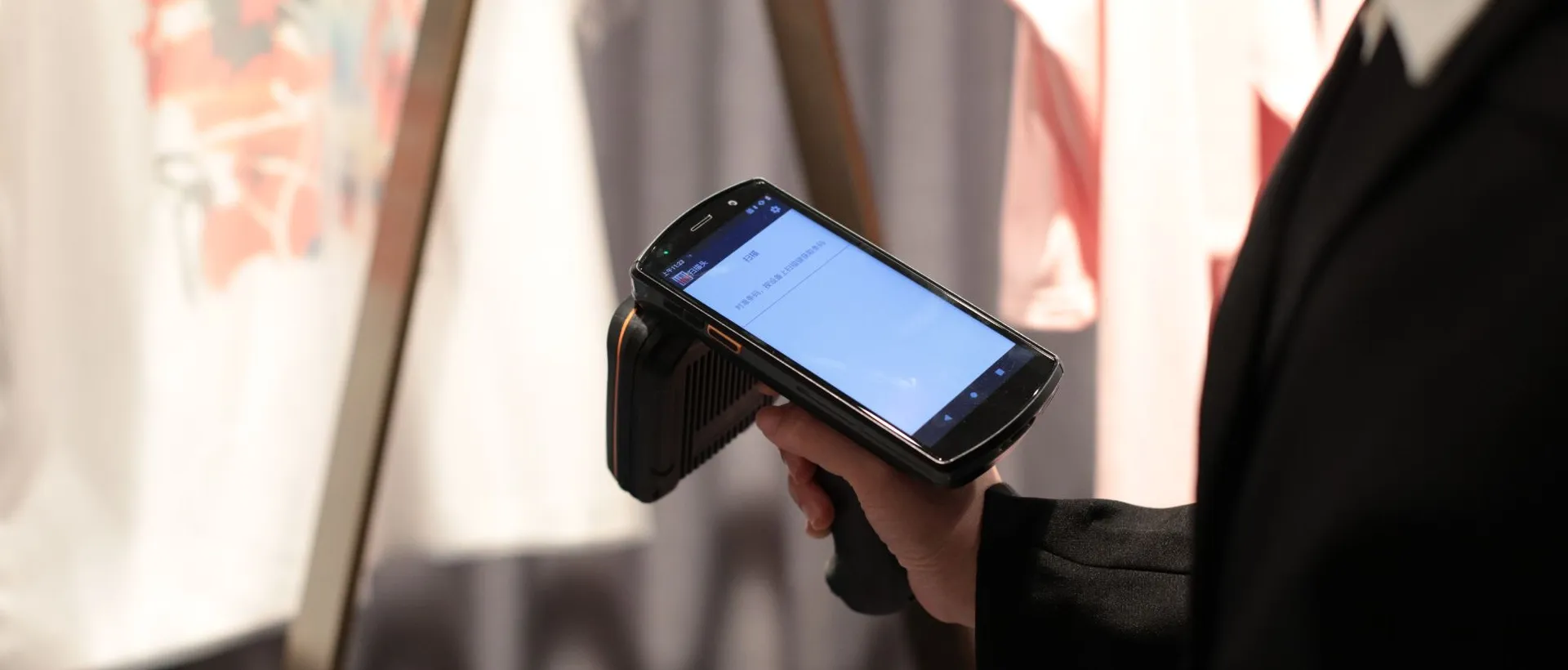
RFID technology leverages radio waves to capture data from tags attached to objects, without the need for a direct line of sight. RFID systems can be categorized into two types: passive and active. Passive RFID tags are powered by the reader's electromagnetic signal, whereas active tags use a built-in battery to broadcast a signal. In business applications, RFID reader can be stationary or mobile, with handheld RFID reader offering flexibility in dynamic environments.Urovo will compare and present both products.
Understanding Barcode Scanner
Barcode technology encodes data in a visual pattern that a reader decodes and transmits to a computer system. Barcode scanners, including handheld barcode scanners, operate by lighting the code with a red light and converting the reflection into data. While they are simpler and generally more cost-effective than RFID systems, they require a direct line of sight to the barcode, potentially limiting their application in certain business contexts.Urovo also provides a detailed selection guide for barcode scanner.
Key Differences Between RFID and Barcode
Data Storage and Capacity
RFID readers have a significant advantage in terms of data storage and transmission capabilities. They can store a wide range of information from serial numbers to other item-specific data in a compact, tamper-proof format. In contrast, barcode scanners can only access data that is directly encoded in the barcode, limiting their functionality to basic identification tasks.
Read Range and Environment Flexibility
RFID technology does not require line-of-sight and can read tags from several meters away, even in challenging environments. This capability is particularly beneficial in industries such as warehouse inventory and retail, where quick and reliable data collection is crucial. Conversely, handheld barcode scanners require a direct line of sight and generally have a shorter read range, which can be impeded by environmental factors such as dirt, moisture, or damage to the barcode itself.
Speed and Efficiency
In scenarios requiring the processing of large volumes of items, mobile RFID readers dramatically outpace barcode scanners. A single RFID reader can process multiple tags simultaneously, whereas barcode scanners must scan each barcode individually. This feature makes RFID systems particularly effective in high-throughput environments that demand efficiency and speed.
Advantages of RFID Reader
- Enhanced Data Collection: RFID readers offer advanced data collection capabilities, enabling the integration of multifaceted information like the date, location, and condition of items, which is crucial for complex supply chains and inventory systems requiring thorough auditing and reporting.
- Improved Inventory and Asset Management: RFID technology allows scanning multiple items simultaneously without requiring direct line-of-sight, leading to quicker and more accurate inventory counts. This capability provides businesses with real-time visibility into their assets, essential for optimizing inventory levels and reducing errors or theft.
- Long-term Cost Benefits and Scalability: Despite higher initial setup costs, the scalability and extensive capabilities of RFID can provide significant long-term cost savings. This technology is particularly beneficial for businesses planning to expand or those with high labor costs associated with manual scanning, offering a substantial return on investment.
Advantages of Barcode Systems
- Cost-Effectiveness and Ease of Implementation: Barcode systems are attractive for small to medium-sized enterprises due to their lower cost and ease of implementation. These systems can be integrated into existing operations with minimal disruption.
- Reliability and Familiarity: Well-established and widely understood, barcode technology offers a reliable solution for businesses seeking a straightforward, proven method for tracking goods. This simplicity reduces the potential for technical issues and the need for specialized training.
- Flexibility and Compatibility: Barcode scanners are highly compatible with existing IT systems and can be easily adapted to various business environments. This adaptability makes barcodes suitable for businesses that require a versatile, user-friendly technology that can be deployed across different operational contexts.

Choosing the Right Technology for Your Business
Selecting between RFID and barcode technology involves considering factors such as budget, the complexity of inventory systems, and long-term business goals. Industries with high-volume transactions or those requiring detailed tracking and data analysis may benefit more from RFID. In contrast, smaller businesses or those with simpler needs may find barcode systems more suitable.Urovo devices offers a wide selection of feature-rich to protect your business.
Feature
RFID
Barcode
Technology Type
Uses radio frequency
Uses optical, visible light
Data Capture
Can read data from a distance
Requires direct line of sight
Data Capacity
Higher capacity, stores more information
Limited data, often numeric or a URL
Speed
Reads multiple tags at once
Scans one code at a time
Cost
Generally more expensive
Less expensive
Durability
More durable, not affected by dirt/oil
Sensitive to physical conditions
Applications
Inventory tracking, security, etc.
Retail, inventory, simple tracking
Conclusion
The choice between RFID readers and barcode scanners should be informed by a clear understanding of each technology's strengths and limitations. By aligning technology selection with strategic business objectives and operational requirements, organizations can enhance efficiency, accuracy, and profitability.